Initially developed in the 1990s as a standardized method of connecting computers with keyboards, displays, and other peripherals, Universal Serial Bus (USB) cables have transformed how electronic devices exchange power and data. USB simplifies and streamlines connections between a wide range of devices and is a necessary component of many tools we use daily.
Today, there are several USB connector types, each of which is further classified according to its power specifications. In this guide, we’ll discuss the most common types of USB connectors and the key selection considerations to help you identify the right product for your needs.
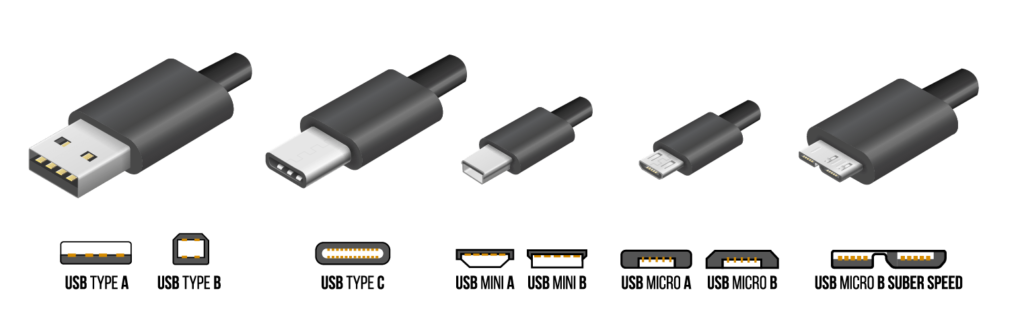
The Most Common USB Connector Types
Modern USB cables facilitate data communication and power delivery and are significantly faster than previous generations. However, they also come in multiple connection types, which are largely incompatible with one another. This makes it essential to identify the right USB type for your device’s port. Below, you can learn more about the different types of USB connectors.
USB A-Type

Widely regarded as the standard connector type, USB Type-A connectors are very common. They feature a flat, rectangular interface that joins directly to host devices, held in place using friction. A-Type connectors are durable enough to establish continuous connections but also user-friendly enough to be easily connected and disconnected. In most cases, IT peripherals have a USB Type-A connector that plugs into a PC. USB A-Type is also available in micro variations.
USB B-Type
USB Type-B connectors have traditionally been used with printer cables but are now more commonly used in cell phones and other peripheral devices like external hard drives. They feature a square interface and are available in several types:
- Micro-USB B
- USB Mini-b (5-pin)
- USB Mini-b (4-pin)
USB Mini-B
Developed in the early 2000s, the USB mini-B features a slim profile and a snug fit. While it was initially used in early smartphones, digital cameras, and GPS navigation systems, it is less popular today due to the rise of micro USB technology.
USB Micro-B
As a very small 5-pin connector, the micro USB connector type is commonly used with small electronics like smartphones, game controllers, and power banks. USB micro-B is also widely used in Android smartphones that lack a USB-C receptacle.
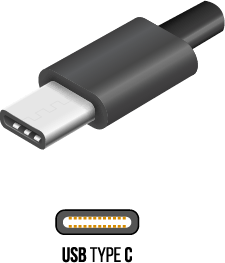
USB C-Type
The newest type of connector, USB C-Type provides a one-size-fits-all solution for replacing older, larger USBs. It features a reversible, symmetrical interface and a sleek, slim design. It can also be adapted to support legacy connectors.
USB Revisions and Specifications
In addition to being categorized by type, USBs are further classified according to their power specifications. Each new version offers increased bandwidth and compatibility with an even broader range of devices and applications.
USB 1.1
While now obsolete, the USB 1.1 was the first widely used consumer USB. It enabled a maximum bandwidth of 12 Mpbs and was compatible with basic devices, like computer mice and keyboards.
USB 2.0
Also known as the high-speed USB, version 2.0 improved the bandwidth to 480 Mbps. This upgrade allows it to be used for higher bandwidth devices, such as transfer cables, adapters, and mass storage equipment. USB 2.0 also features backward compatibility with USB 1.1 devices.
USB 3.0 (aka USB 3.1 Gen 1)
Referred to as the SuperSpeed USB, 3.0 offers bandwidth improvements, jumping to a maximum of 4.8 Gbps. It also offers backward compatibility with legacy devices.
USB 3.1 (aka USB 3.1 Gen 2)
USB 3.1 can be identified by the switch to blue connectors. These products are capable of transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps and have been incorporated into products like the Apple MacBook.
USB 3.2
Updates have enabled these USB-C connectors to achieve 20 Gpbs.
USB 4.0 (aka USB4)
Initially launched in 2019 with a maximum data transfer rate of 40 Gbps, USB 4.0 connectors output a power of 100 watts. These USB-C cables feature the SuperSpeed logo, SS40, which stands for SuperSpeed 40 Gbps.
USB4 Version 2
The latest version of this specification, launched in 2022, features the highest-ever data transfer rate: 120 Gbps. Since this version is still very new, these USB-C cables may not be easily purchased yet.
USB Power Delivery Standards
With each USB advancement, devices achieve enhanced power delivery standards and improved communication capabilities.
| USB 1.1 | USB 2.0 | USB 3.0 | USB 3.1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Also Known As | USB 3.1 Gen 1 | USB 3.1 Gen 2 | ||
| Release Date | 1998 | 2000 | 2008 | 2013 |
| Speed/Transfer | Full Speed | High Speed | SuperSpeed | SuperSpeed |
| Rate | 12 Mbit/s | 480 Mbit/s | 5 Gbit/s | 10 Gbit/s |
| Power | N/A | 5V, 1.8A | 5V, 1.8A | 20V, 5A |
| Max Cable Length | 3 Meters (9’10”) | 5 Meters (16’5”) | 3 Meters (9’10”) | 3 Meters (9’10”) |
USB Type-C
As discussed earlier, newer developments in USBs offer a simple and comprehensive solution for data transfer and power supply for any device. A USB Type-C connector fits into one multi-use port to charge multiple devices simultaneously. It also offers backward compatibility to support previous USB standards (2.0, 3.0, and 3.1).
Type-C 3.1 features a reversible cable that enables two-way data and power transfer, along with 10 Gbps bandwidth and power up to 20 V at 5 Amps, or a total of 100 W. This is enough power to charge a laptop or operate a 4K monitor. Since this technology is nonproprietary, USB Type-C connectors are quickly becoming the new standard for many operating systems. For example, Intel’s Thunderbolt switched to USB Type-C ports while remaining compatible with USB 3.1. Apple MacBooks also now feature Type-C ports.
Important Considerations When Choosing a USB Cable
Selecting the right USB cable requires consideration of several factors, such as:
- Cable length: If the cable length is too long, USB signals can deteriorate and significantly impact usability. However, the ideal length varies based on type.
- Data transfer speed: USB cables must be able to deliver the transfer speeds needed to accomplish the tasks you’re performing. For example, USB 2.0 is fine for basic needs, but USB 3.0 and above is better for faster file transfer. Check your device’s data transfer capabilities and consider the cable’s frequency of use before deciding on a USB cable.
- Durability: Cables that will be used frequently, such as charging cables, must be more durable than those only intended to be used occasionally. Durable cables usually have reinforced connectors and/or braided exteriors.
- Certifications: USB cables can be tested according to USB-IF quality standards. Certified cables will offer a descriptive bandwidth and power rating.
- Trusted manufacturer: Get USB cables from trusted manufacturers that can meet your data transfer and charging needs. Well-constructed USB connectors offer longer and more reliable service.
High-Quality USB Cables from Consolidated Electronic Wire & Cable
Consolidated Electronic Wire & Cable has over 100 years of experience delivering high-quality cable solutions. In addition to offering an extensive collection of standard USB connectors, we also create custom USB-C cables according to diverse data transfer and charging needs. Contact our team to learn more.
Watch the video!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Below, you can explore some of the most common questions our team is asked about USB cables. If you’re looking for information not listed here, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us—we’re happy to help.




 () Quote Cart
() Quote Cart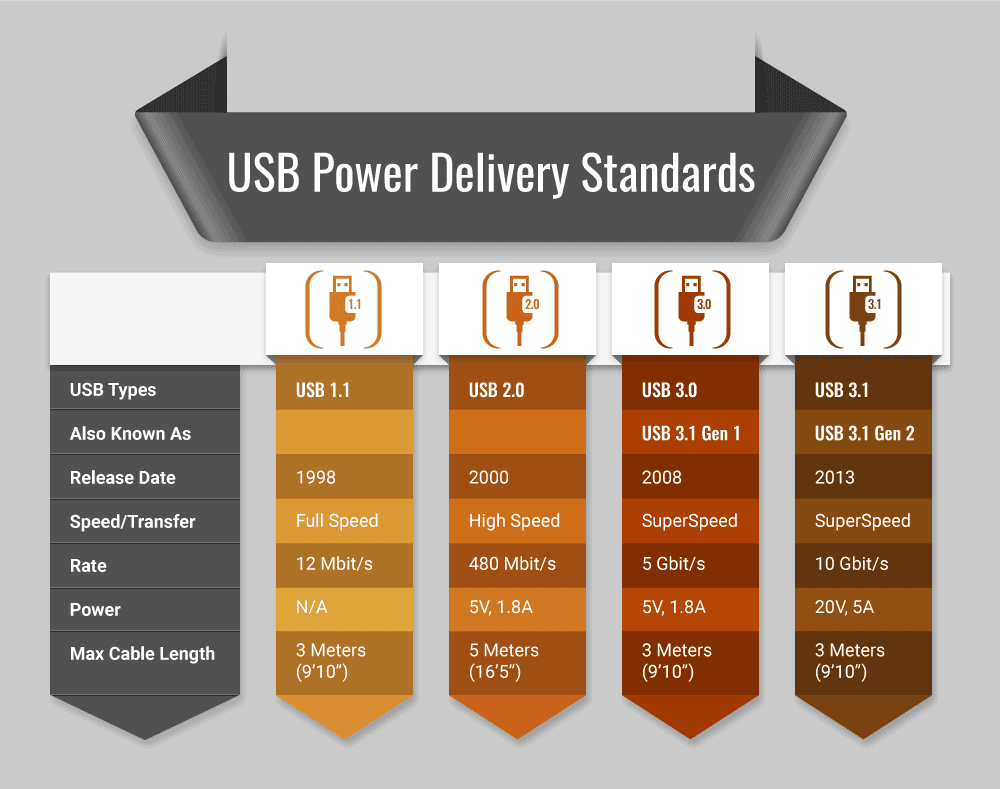



Comments are closed